Það eru tvær algengar gerðir af DC mótorum: burstaðir mótorar og burstalausir mótorar (eða BLDC mótorar). Eins og nafnið gefur til kynna eru brostnir DC-mótorar með bursta sem snúa og snúa mótornum, en burstalausir mótorar skipta út vélræna breytingarhlutverkið með rafrænni stýringu.
Báðar gerðir mótoranna byggja á sömu meginreglu um aðdrátt og frávik spólna og varanlegra segulmanna. Hér er kynning á muninum á mótorunum.
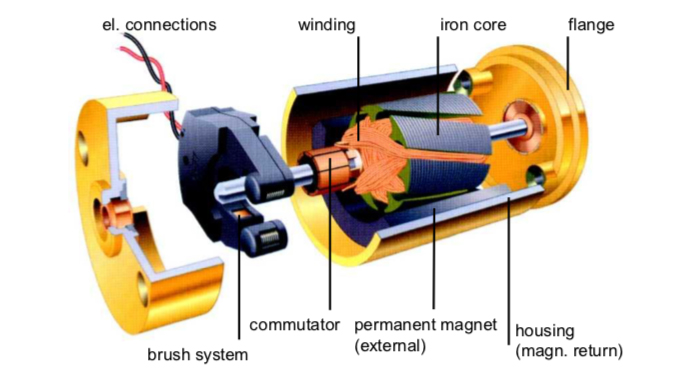
Aðal uppbygging brúninn DC mótor Hann samanstendur af stator, rotor og bursta. Hann framleiðir snúningsnúmer í gegnum snúandi segulsvið og gefur þar með fram hreyfingarorku. Burstarnir berast stöðugt við og nudda á breytinn, sem auðveldar leiðbeiningu og breytingu við snúning.
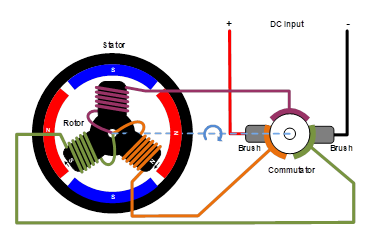
Það er mekaniskur reifni milli brúsanna og samskiptara í brústökuhringi. Þar sem þetta eru rafmagnsamskiptapunktir, geta þeir ákveðið ekki verið smásættir, og það krefst tímarlega skiptis af kolbrúsunum.
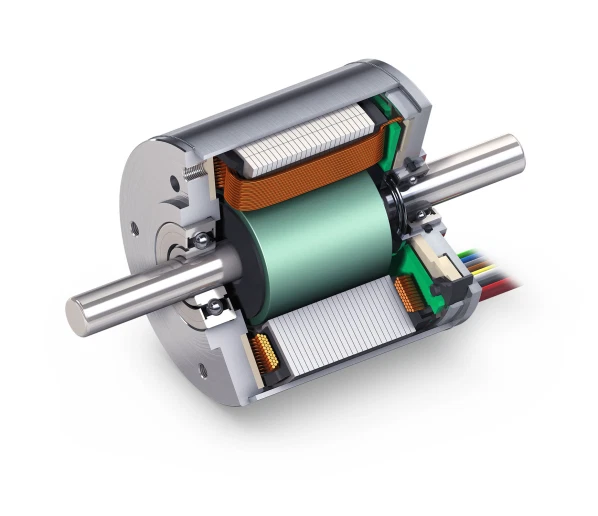
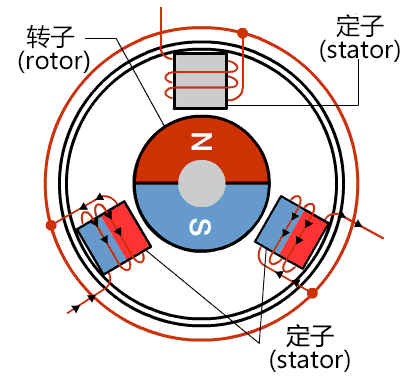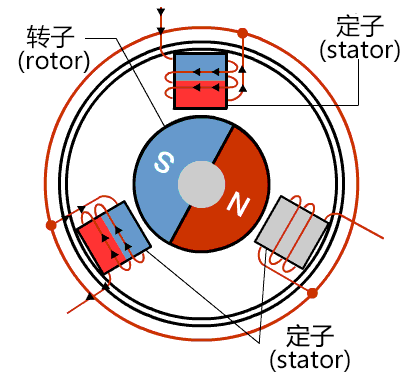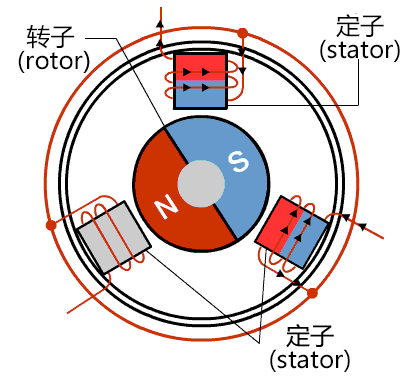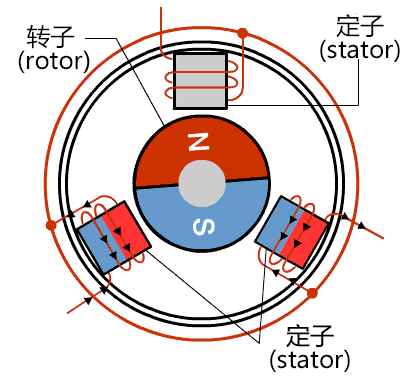
The grunnreglulegur hluti magnabrekka og afstöðu í brúlausum DC hringsvæðimotörum er sama og fyrir brústökuhringi, en stöðurnar þeirra eru eitthvað ólíkar. Á móti því að brústökuhringar noti mekanískan samskiptara og brús, ná öflug hringsvæðismotörar snúningnum á samskiptara hringsvæðisins með rafrænri samskiptara, sem krefst virkjarstýringar. Í brúlausum DC hringsvæðimotörum er samskipta hafinn fram við stýrsluskrám sem eru innbyggðar í stýri, oft með Hall-sensors og stýri, eða meira frumvarpandi teknologi eins og magnamæliköppum.

Krafalrík DC-mótorker fyrir hvernig elektrónskt umskeiða, þar sem spolarnar eiga að vera stilltar og magnúsipólarnir snúa. Þessi mótorker notar mengi af elektrónskum tækjum, þátturinn Hall-víkjandi SS2712 til að athuga staðsetningu fastra magnúsipóla. Á grunn þessa athugunar, skipta elektrónskir kringlætir áttina á straum í spólunum í réttu tíma til að tryggja framleiðslu magnúsakrafta í réttri átt til að keyra mótorn. Þessi útlit gerir burtu við nákvæmni krafalríkra DC-móta.
Fylgjandi töflu er samanburður milli krafalríkra DC-móta (BLDC mótor) og krafalríkra DC-móta:
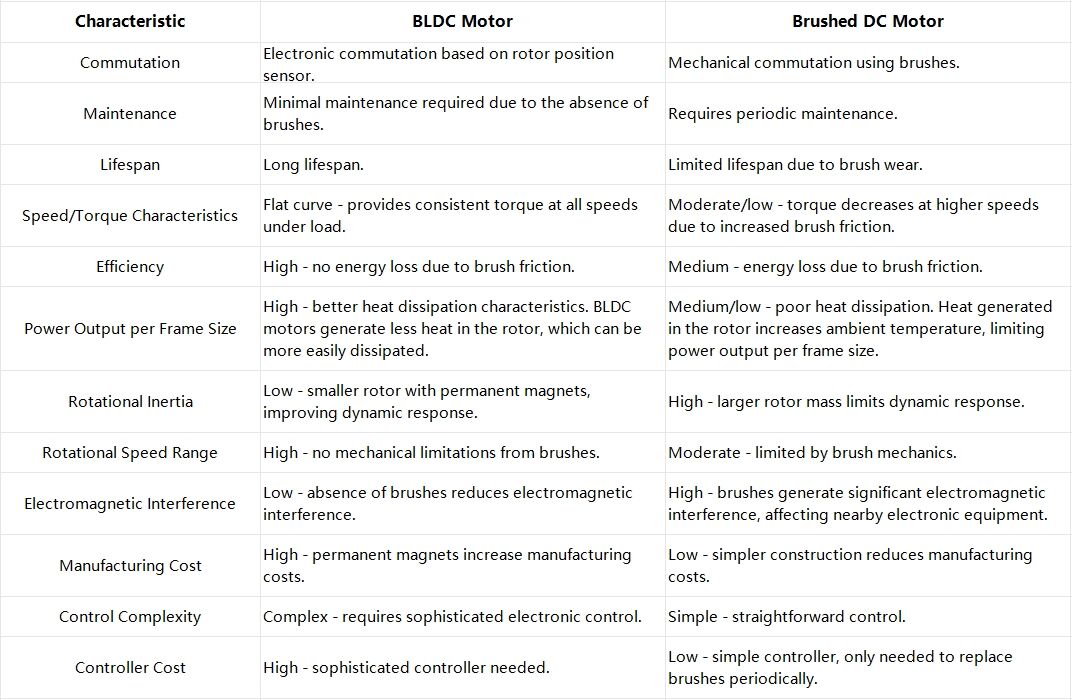
Þó að krafalrík DC-mótorker (BLDC mótor) séu dýrari og flóknari en krafalríkir DC-mótar, þeir bjóða mörgum kostnaði yfir krafalríka móta í öðrum hlutum:
Eftir því sem kostnaður á óbürabrýnenda DC-mótornum (BLDC-mótormum) og tengdri elektroník komast í lægri stöðu, eru BLDC-mótarinnir aukin að fara inn í vöruvörðun sem hefðu verið trúðar af bürabrýnenda mótorum. Þeir nota þau auka í húsgerð, bílaverkefnum, rymdisflug, notendagögnum, líffræðilegu tækjum, efnahagsstýringartækinu og mælingaraðferðum.
 Heitar fréttir
Heitar fréttir 2024-05-14
2024-04-22
2024-04-07